Velamen layer in orchids
Last reviewed: 29.06.2025
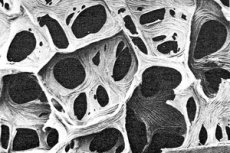
Velamen is a special tissue layer covering the roots of orchids. This layer plays a crucial role in adapting orchids to their epiphytic lifestyle, enabling efficient absorption of water and nutrients from the environment. Let’s explore its functions, structure, and importance to the plant in detail.
What is velamen?
Velamen is a multi-layered spongy tissue that covers orchid roots. It consists of dead cells with thick walls, giving it unique properties. Velamen allows orchid roots to function as a "reservoir" for water and nutrients, which is especially critical for epiphytic plants growing on trees with limited access to soil and moisture.
Structure of velamen
- Outer layer:
- Made up of thick-walled dead cells.
- These cells are transparent and act like a sponge to absorb water.
- Inner layer (beneath the velamen):
- Contains living cells that actively transport water and nutrients to the plant.
- Air spaces:
- Velamen has numerous microscopic pores and air pockets, making the roots lightweight and improving ventilation.
- Cuticle coating:
- The outer surface may have a thin cuticle layer to protect the roots from dehydration.
Key functions of velamen
- Water absorption:
- Velamen can absorb moisture from rain, dew, or humid air.
- Water quickly penetrates the velamen through capillaries.
- Water and nutrient storage:
- Velamen acts as a reservoir for water and dissolved nutrients, sustaining the plant during dry periods.
- Root protection:
- Dead cells in the velamen shield the living tissue underneath from damage.
- Its porous structure minimizes excessive water loss.
- Photosynthesis participation:
- In some orchids, velamen is transparent, allowing light to reach green tissues in the roots, where photosynthesis occurs.
- Attachment to surfaces:
- Velamen enables orchid roots to firmly attach to tree bark, rocks, or other substrates.
How velamen helps orchids survive in nature?
Orchids, particularly epiphytic species, often grow on trees where soil access is unavailable. Velamen compensates for this by enabling orchids to:
- Capture moisture from the surrounding air.
- Absorb nutrients from decomposing organic matter on tree surfaces.
- Withstand dry periods by storing water.
Velamen color and root health
The color of velamen is a key indicator of root health:
- Silvery-white: normal state. The roots are dry and ready to absorb water.
- Green: indicates that the root is hydrated and photosynthesis is active.
- Brown or black: a sign of rot or root damage.
How velamen responds to environmental conditions?
- High humidity: velamen becomes saturated with water, and roots turn green.
- Dry air: velamen dries out, returning the roots to their silvery-white color.
- Damage: if velamen is damaged, the root's ability to absorb water is significantly reduced.
How to care for orchids with velamen in mind?
- Watering:
- Water the orchid when the roots turn silvery-white.
- Ensure that water drains completely to avoid root rot.
- Lighting:
- Provide adequate light for velamen-covered roots to contribute to photosynthesis.
- Humidity:
- Maintain humidity levels between 50–70% for optimal velamen function.
- Water quality:
- Use soft or filtered water. Hard water salts can clog velamen pores.
- Substrate:
- Choose bark, sphagnum moss, or another porous substrate that allows velamen to breathe.
Interesting facts about velamen
- Orchids aren’t the only plants with velamen. This adaptation is also found in some other epiphytic plants.
- The thickness and structure of velamen can vary depending on the orchid species and its natural habitat.
- Research on velamen inspires the development of new materials that mimic its water absorption and storage capabilities.
Conclusion
The velamen layer is a unique and multifunctional adaptation that allows orchids to thrive in challenging natural environments. Understanding its structure and functions helps provide optimal care for orchids at home. By considering velamen's needs, you can ensure your orchids remain healthy and beautiful.
